Introduction
Protein is often called the building block of life—and for good reason. From repairing tissues and fueling muscle growth to supporting hormones and enzymes, protein is essential for nearly every function in the human body. But despite its importance, most people either underestimate or overestimate how much protein they need daily.

In this article, we’ll break down why protein intake matters, how much you actually need depending on your lifestyle, and how our Protein Intake Calculator can help you find the right balance for your health and fitness goals.
Why Protein Intake Matters
Protein does far more than just help gym enthusiasts build muscle. It’s vital for:
- Muscle repair & growth – Essential after workouts or physical activity.
- Weight management – High-protein diets keep you fuller for longer, reducing overeating.
- Metabolism boost – Digesting protein burns more calories compared to carbs and fats.
- Immune support – Antibodies that fight infections are made of protein.
- Healthy aging – Adequate protein helps prevent muscle loss (sarcopenia) as you age.
Without sufficient protein, you risk fatigue, muscle weakness, poor recovery, and weakened immunity.
How Much Protein Do You Need?
General Recommendations
- Sedentary adults: ~0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight per day.
- Active individuals: 1.2 – 2.0 grams per kilogram of body weight.
- Strength athletes & bodybuilders: Up to 2.2 grams per kilogram.
- Older adults: Slightly higher protein (1.0 – 1.2 g/kg) to preserve muscle mass.
👉 Example: A 70 kg person who exercises regularly may need 84–140 g protein/day.
Factors That Influence Protein Needs
- Body Weight & Composition – Larger body mass = higher protein demand.
- Activity Level – More activity requires more repair and growth.
- Age – Older adults need more to combat muscle decline.
- Fitness Goals – Fat loss, maintenance, or muscle gain all impact protein requirements.
- Health Conditions – Certain illnesses or recovery from surgery may increase needs.
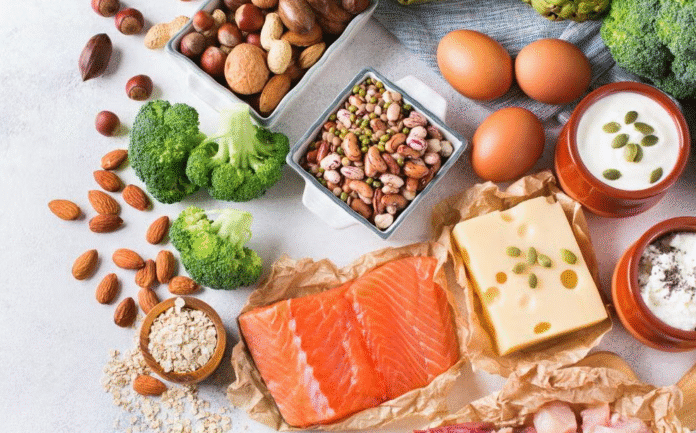
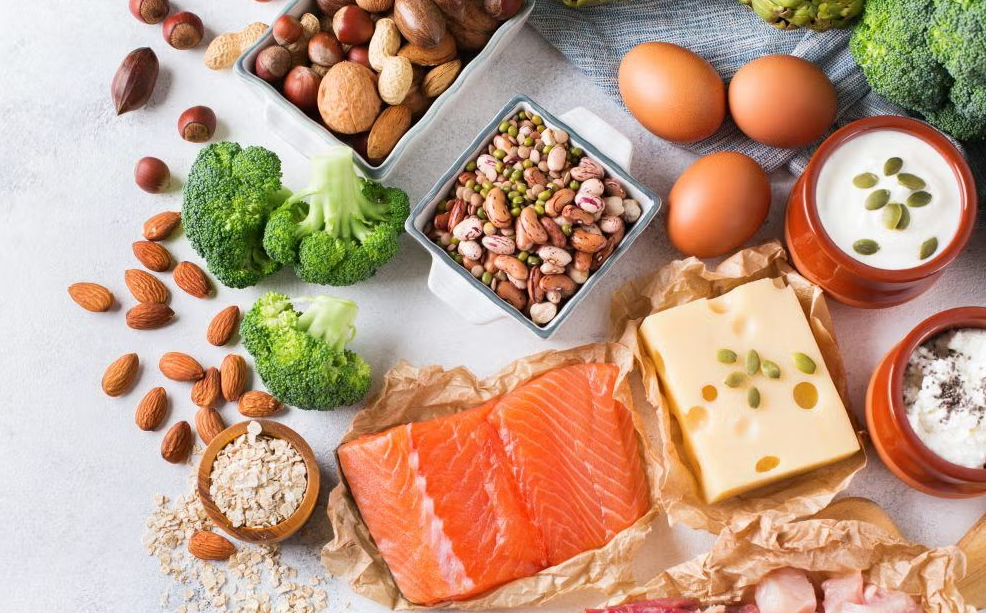
Best Sources of Protein
Animal-Based
- Eggs
- Lean chicken, turkey, fish
- Dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese)
Plant-Based
- Lentils, chickpeas, beans
- Quinoa, soy, tofu, tempeh
- Nuts & seeds
💡 Pro Tip: Combining different plant proteins (e.g., rice + beans) ensures you get all essential amino acids.
Common Myths About Protein
- ❌ “High protein damages kidneys” – True only if you already have kidney disease.
- ❌ “You can’t get enough protein on a vegetarian diet” – Many plant sources provide sufficient protein when planned well.
- ❌ “More protein is always better” – Excess doesn’t mean more muscle; balance is key.
Why Use a Protein Intake Calculator?
Instead of guessing your protein needs, our Protein Intake Calculator uses your weight, activity level, and goals to provide a personalized daily protein target.
This helps you:
- Avoid under-eating protein (leading to weakness).
- Avoid over-eating (wasting calories).
- Align your diet with your fitness, weight loss, or muscle-gain goals.
Conclusion
Protein is a cornerstone of good nutrition. Whether you’re aiming to build muscle, lose weight, or simply maintain overall health, getting the right amount of protein is non-negotiable. Instead of relying on one-size-fits-all advice, use our Protein Intake Calculator to discover your exact daily protein needs and take control of your nutrition.